This guide simplifies transformer wiring, crucial for safety and reliable operation across all applications. It covers essential concepts, step-by-step procedures, and critical safety precautions. Master connections for proper electricity delivery and equipment protection, ensuring efficient and safe setup.
Importance of Safe and Reliable Wiring
Ensuring safe and reliable transformer wiring is paramount, whether dealing with a small appliance or large industrial equipment. Improper wiring can lead to severe consequences, including electrical hazards, equipment damage, and operational failures. This fundamental principle underpins the entire electrical system’s integrity and longevity. A correctly wired transformer guarantees not only the safety of personnel but also the protection of valuable assets. It prevents overheating, short circuits, and other dangerous conditions that could result in costly repairs or even catastrophic incidents. Reliable wiring ensures consistent and stable power delivery, which is vital for the uninterrupted functioning of connected loads. Fluctuations or interruptions caused by faulty connections can disrupt critical processes, leading to significant downtime and financial losses. Adhering to established safety protocols and wiring standards, such as those covered in this guide, is therefore non-negotiable. It ensures that the transformer operates within its design parameters, providing efficient energy conversion. Furthermore, reliable connections contribute to the overall efficiency of the electrical system, minimizing energy waste and maximizing performance. Proper installation, including adherence to lockout tagout (LOTO) procedures and correct grounding, significantly mitigates risks. Ultimately, investing time and effort into safe and reliable wiring practices safeguards lives, equipment, and operational continuity, making it a critical aspect of electrical installations.
Guide Objectives: Safety, Reliability, and Operation
This guide’s primary objectives are to empower users with the knowledge and skills necessary for safe, reliable, and efficient transformer operation. Firstly, safety is paramount; the guide aims to instill critical safety precautions and protocols, ensuring protection for both personnel and equipment throughout the wiring process. This includes understanding potential hazards and implementing preventative measures, such as lockout tagout (LOTO), to mitigate risks before, during, and after installation. Secondly, it focuses on achieving utmost reliability in transformer connections. By detailing proper wiring techniques and emphasizing adherence to specifications and ratings, the guide ensures stable power delivery and prevents malfunctions. The goal is to establish robust and durable connections that minimize downtime and maintenance requirements. Lastly, the guide seeks to optimize transformer operation. It provides insights into how correct wiring influences performance, efficiency, and the lifespan of the unit. Users will learn to make connections that support the transformer’s intended function, whether for voltage transformation, current measurement, or other specific applications. This holistic approach ensures that transformers are not just wired, but wired correctly for sustained, dependable, and optimal performance, providing a comprehensive resource for all levels of expertise.

Overview of Essential Concepts and Procedures
This guide presents a comprehensive overview of essential concepts and practical procedures for transformer wiring. It begins by establishing fundamental principles governing transformer operation, providing a solid theoretical foundation. A key section focuses on interpreting wiring diagrams, teaching users to accurately read schematics, identify critical components, and understand specifications and ratings crucial for proper installation. The guide then details general step-by-step wiring instructions, outlining the systematic approach required for safe, reliable connections. Emphasis is placed on ensuring proper wire paths, correctly identifying terminals, and making secure connections across diverse applications. It further highlights how precise wiring is indispensable for accurate current measurement, stable voltage delivery, and robust protection within electrical systems. By covering these core concepts and methodical procedures, this resource aims to equip individuals with knowledge to confidently execute transformer wiring, guaranteeing optimal long-term performance and system integrity.

Fundamental Transformer Concepts
Transformers operate on the principle of mutual induction between their primary and secondary windings. The primary side connects to the AC power source, receiving input voltage, while the secondary side delivers the transformed output voltage to the load. Understanding these core concepts is vital.
Principle of Mutual Induction
Transformers fundamentally operate on the principle of mutual induction, a crucial electromagnetic phenomenon. This principle dictates that a changing current in one coil, known as the primary winding, generates a fluctuating magnetic field. This magnetic field, in turn, links with a second, adjacent coil, the secondary winding, through a common magnetic core. As the primary coil’s magnetic field expands and collapses due to the alternating current, it cuts across the turns of the secondary coil. This action induces an electromotive force (EMF), or voltage, in the secondary winding, even though there is no direct electrical connection between the two coils. The efficiency of this magnetic linkage is significantly enhanced by the ferromagnetic core, which concentrates the magnetic flux, ensuring nearly all the magnetic field produced by the primary coil passes through the secondary coil. This elegant mechanism allows for the transfer of electrical energy from the primary circuit to the secondary circuit, with a change in voltage level, forming the very foundation of how transformers function to step up or step down AC voltages for various applications, from household appliances to industrial power distribution systems, ensuring electrical compatibility and safety across diverse networks. The number of turns in each winding determines the voltage transformation ratio.

Primary and Secondary Winding Connections
The primary and secondary windings are the fundamental components defining a transformer’s electrical interface. The primary side consistently connects to the incoming power source, where it receives the initial input voltage. This connection is vital for establishing the alternating magnetic field within the transformer’s core. In contrast, the secondary side is dedicated to delivering the transformed voltage to the connected load, which could range from sensitive electronic devices to robust industrial machinery. The crucial distinction lies in their roles: one receives energy, the other delivers it at a modified voltage level.
Proper wiring of these respective sides is absolutely paramount for safe and reliable transformer operation. Errors in connecting the primary to the load or the secondary to the source, or incorrect phasing, can result in severe consequences such as damage to the transformer, connected equipment, or even electrical hazards. Identifying the specific terminals, typically marked (e.g., H1, H2 for primary and X1, X2 for secondary on single-phase units), is a foundational step. Adherence to detailed wiring diagrams, which specify voltage ratings and terminal configurations, ensures the unit functions correctly, providing the intended voltage transformation and maintaining system integrity.
Understanding Input and Output Voltage
A fundamental aspect of transformer wiring involves a clear comprehension of input and output voltages. The input voltage, also known as the primary voltage, is the electrical potential supplied to the primary winding from the power source. This voltage initiates the magnetic flux that facilitates energy transfer. Conversely, the output voltage, or secondary voltage, is the transformed electrical potential available at the secondary winding, which then supplies the connected load. Transformers are designed to either “step up” or “step down” this voltage, depending on the ratio of turns in their windings.
For instance, a transformer might convert a 240V circuit input to a 120V output for a mill power feed, or transform a 575 Volts Delta primary to a 460Y/266 Volts secondary for industrial applications. Understanding these specific voltage ratings (e.g., 120/277V, 12-24VDC) is crucial. Incorrectly matching the transformer’s input voltage to the supply, or its output voltage to the load’s requirements, can lead to severe damage to both the transformer and the equipment it powers. Proper selection ensures the transformer effectively converts the local mains voltage to the appropriate operating voltage for the intended application, guaranteeing efficient and safe electrical delivery.

Critical Safety Measures for Wiring
Implementing critical safety measures is paramount when wiring transformers. Strict adherence to protocols before, during, and after the process is essential. Essential precautions like Lockout Tagout (LOTO) protect both personnel and equipment, ensuring a safe and reliable electrical installation for all operations.
Essential Safety Precautions and Protocols
Wiring transformers demands strict adherence to essential safety precautions and established rigorous protocols to safeguard both equipment and personnel. Before commencing any work, conducting thorough arrival inspections is paramount, including checking for damage, gas pressure, core insulation integrity, and moisture levels. Always confirm all power sources are completely disconnected and de-energized. This critical step effectively prevents accidental energization during the wiring process.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) such as insulated gloves, safety glasses, and appropriate footwear must be consistently worn. Rigorously follow all local electrical codes and regulations, including the National Electrical Code (NEC). Implementing a robust Lockout Tagout (LOTO) procedure is absolutely non-negotiable; this physically isolates energy sources and prevents unauthorized reactivation, thereby protecting workers from hazardous energy releases. Proper LOTO application is a cornerstone of electrical safety.
Ensure the work area is clear and well-lit. Never work alone on energized circuits. Always verify connections using appropriate testing equipment before re-energizing. These collective protocols prevent accidents, ensure reliable operation, and provide comprehensive protection for everyone involved in transformer wiring tasks. Adhering strictly to these guidelines is fundamental for a safe and successful installation.
Implementing Lockout Tagout (LOTO)
Implementing Lockout Tagout (LOTO) is a non-negotiable safety protocol paramount for safeguarding personnel during transformer wiring. This rigorous procedure ensures that all energy sources are completely isolated and rendered inoperative, preventing accidental energization while work is being performed. The LOTO process begins with identifying all potential energy sources and notifying affected personnel of the impending shutdown. Next, the equipment must be safely shut down according to established operational procedures. Subsequently, energy-isolating devices, such as circuit breakers or disconnect switches, are physically operated to disconnect the transformer from its power supply. After isolation, individual lockout devices, typically padlocks, are applied to the energy-isolating devices, ensuring they cannot be inadvertently reactivated. Concurrently, tags are affixed, clearly indicating that the equipment is locked out, the reason for the lockout, and the identity of the authorized person. A critical final step involves verifying the isolation by attempting to start or operate the transformer, confirming that it is indeed de-energized. This comprehensive LOTO protocol, central to engineer-level safety, is essential for mitigating risks like electric shock and arc flash, thereby ensuring a safe working environment and protecting equipment integrity during all wiring procedures.
Protecting Equipment and Personnel
Protecting equipment and personnel during transformer wiring is paramount, extending beyond Lockout Tagout protocols. Essential safety precautions begin with the mandatory use of appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), including insulated gloves, safety glasses, arc-rated clothing, and non-conductive footwear to guard against electrical hazards. Establishing a clear, clean, and dry work area free from obstructions and potential slip hazards is crucial. All tools used must be in good condition, properly insulated, and suitable for electrical work to prevent accidental contact with live components.
Furthermore, implementing robust circuit protection mechanisms such as fuses and circuit breakers is vital to safeguard the transformer and connected load from overcurrents, short circuits, and faults, thereby preventing damage and potential fires. Strict adherence to local and national electrical codes, like the NEC, ensures installations meet minimum safety standards for system reliability and personnel protection. Proper grounding, although detailed elsewhere, fundamentally contributes to safety by providing a safe path for fault currents. Thorough pre-energization inspections and testing are also critical steps to verify correct connections and identify any potential issues before power is applied, preventing damage to the transformer and ensuring operator safety. Continuous training and awareness for all personnel involved further enhance overall safety culture and operational accuracy, reducing risks in all wiring procedures.
Interpreting Transformer Wiring Diagrams
Interpreting transformer wiring diagrams is fundamental for correct and safe installation. This section guides you through reading diagrams, identifying components and connections, and understanding crucial specifications and ratings for successful transformer setup.
How to Read Wiring Diagrams
Reading electrical diagrams is a critical skill for any transformer installation. Begin by familiarizing yourself with standard electrical symbols, which represent various components like windings, switches, and protective devices. Look for primary (H) and secondary (X) winding terminals, often labeled to indicate input and output connections. Diagrams typically detail voltage ratings, such as 575 Volts Delta primary or 460Y/266 Volts secondary, and may include tap settings like 1-5 ANFC and BNFC for voltage adjustments. Trace wire paths carefully from the power source to the primary side, and from the secondary side to the load, paying close attention to connection types (e.g., Delta, Wye). Identify all components, their specific labels, and interconnections, which are essential for understanding the circuit’s function and ensuring correct wiring. These drawings provide crucial details of the transformer, switchgear, and associated components. Always refer to the legend or accompanying documentation for symbol interpretations and specific instructions. Proper interpretation allows for accurate current measurement, protection, and overall system safety and reliability, preventing errors during installation or troubleshooting. Understanding the flow and configuration depicted is paramount for achieving a successful and safe setup, aligning with design specifications and operational requirements.
Identifying Components and Connections
Identifying transformer components and connections is foundational for safe and effective wiring. Begin by locating the primary and secondary windings, typically labeled ‘H’ for high voltage (primary) and ‘X’ for low voltage (secondary). The primary side connects directly to the power source, receiving the input voltage, while the secondary side delivers the transformed voltage to the load. Look for dedicated grounding terminals or lugs on the transformer enclosure, crucial for safety and system protection. Wiring diagrams are indispensable, detailing the transformer itself, associated switchgear, and other circuit components. They clearly show labeling and interconnections, outlining wire paths and connection types such as Delta or Wye configurations. Pay close attention to terminal labels and any accompanying specifications found on the transformer’s nameplate or installation guide; Understanding these components—from the main windings to auxiliary elements like current and voltage transformer connections—ensures proper functionality. Identifying each element and its role within the overall circuit design is key. This meticulous approach guarantees correct installation, reliable electricity delivery, and adherence to design specifications for both AC and DC applications, preventing miswirings that could lead to equipment damage or safety hazards. Always consult the principal wiring diagram on the label or in the manual.
Understanding Specifications and Ratings
Understanding transformer specifications and ratings is paramount for correct installation and safe operation. These critical details, typically found on the transformer’s nameplate or within its accompanying documentation, dictate its precise operational parameters. Key specifications include primary and secondary voltage ratings, such as 575 Volts Delta primary and 460Y/266 Volts secondary, which define the input and output voltage capabilities. Current ratings (amperes) for both windings are also crucial to ensure appropriate wire sizing and overcurrent protection. The kVA or MVA rating indicates the transformer’s overall power handling capacity. Winding configurations, like Delta or Wye, are vital for system compatibility and fault characteristics. Taps, often labeled ANFC (Above Normal Full Capacity) or BNFC (Below Normal Full Capacity), provide flexibility for minor voltage adjustments. For specialized current and voltage transformers (CT/VT), understanding the burden rating is essential to ensure accurate measurement and protection. These ratings help in selecting appropriate conductors, setting protective devices, and verifying that the transformer is suitable for the intended application. Ignoring these specifications can lead to overheating, inefficiency, equipment damage, or hazardous conditions. Always refer to the specific model’s installation guide for precise details, ensuring system safety and accuracy.

Step-by-Step Wiring Procedures
Follow clear, step-by-step wiring procedures for safe, efficient transformer installation. Always consult the principal wiring diagram on the label for connection layouts, labeled terminals, and wire paths. Proper wiring ensures reliable operation and accurate setup.
General Wiring Instructions
Wiring a transformer, whether for a small home appliance or large industrial equipment, is a critical task that, while seemingly complex, becomes manageable with foundational understanding. This guide aims to simplify the process, ensuring safe and proper operation. A key initial step involves thoroughly reviewing the specific installation and wiring instructions provided with your transformer model. These manufacturer-specific bulletins often contain vital details, including connection layouts, labeled terminals, and recommended wire paths. Always refer to the principal wiring diagram found on the transformer’s label or in its accompanying manual. This diagram is your primary reference for identifying connection types and key components, guiding you through each step. Clear, systematic execution of these instructions is paramount. Ensure every connection is secure and accurately follows the designated path. This meticulous approach guarantees proper electricity delivery and safeguards both equipment and personnel. Remember, the goal is a reliable and safe setup in all AC and DC applications. Adhering to these general principles makes the task much more straightforward.
Connecting Primary and Secondary Sides
Connecting the primary and secondary sides is vital for transformer operation and energy transformation. The primary winding connects to the AC power source, receiving input power. Identify primary terminals (H1, H2, H3) and match supply voltage to the transformer’s rating. Always consult wiring diagrams for configurations (e.g., 575 Volts Delta), as incorrect voltage application causes severe damage.
The secondary winding connects to the electrical load, delivering transformed voltage. Its terminals (e.g., X1, X2, X3, X0) accommodate various multi-phase or single-phase setups (e.g., 460Y/266 Volts secondary). Converting a 240V circuit for a 120V load requires precise secondary connections per the diagram. This ensures proper phase rotation and reliable voltage supply. Securely fastening all primary and secondary leads is paramount for operational safety, accurate measurement, and efficient energy transfer.
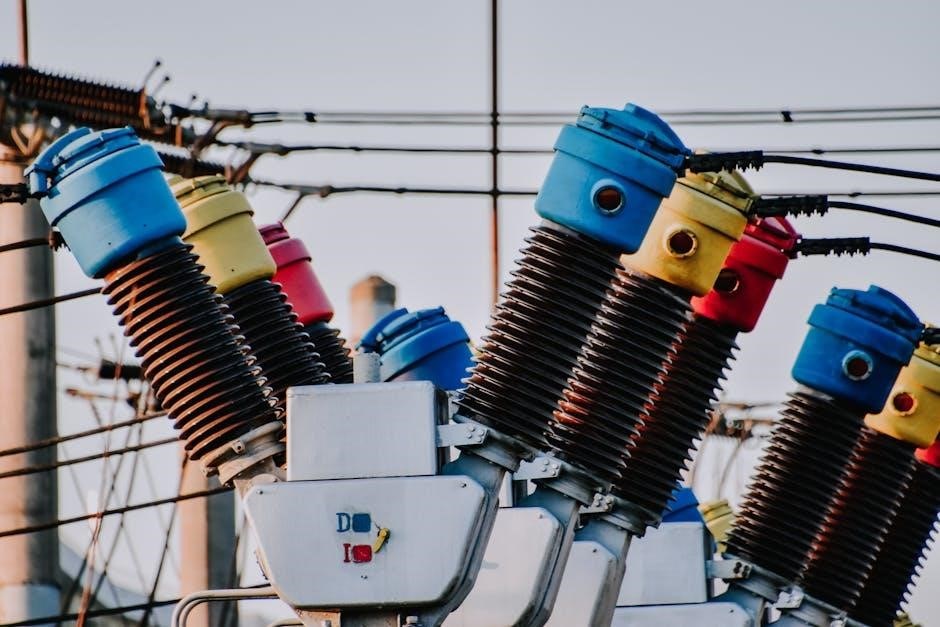

Ensuring Proper Connections and Wire Paths

Ensuring proper connections and meticulously planned wire paths is paramount for any transformer installation. Always refer to the principal wiring diagram found on the transformer’s label or within its dedicated installation guide. These diagrams provide a clear connection layout, detailing labeled terminals, specific wire paths, and essential configuration tips for safe and accurate setup in various AC and DC applications.
Before making any connections, thoroughly inspect all wires for damage and ensure they precisely match the specifications outlined in the diagram. Pay close attention to insulation integrity. When routing wires, maintain adequate separation to prevent interference and overheating. Avoid sharp bends or kinks that could damage conductors. Secure all connections firmly to prevent loose contacts, which can lead to arcing, overheating, and potential equipment failure.
Verify continuity with a multimeter after wiring to confirm correct paths and the absence of short circuits. This critical step aids troubleshooting before energizing the transformer, ensuring efficient operation and extending the unit’s lifespan, protecting both personnel and connected equipment.

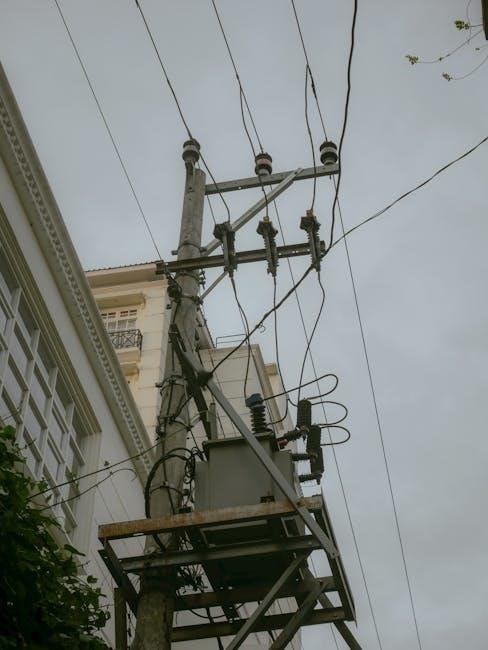
Transformer Grounding and Specific Applications
This section covers vital transformer grounding, including terminal identification and conductor selection. It details wiring for current and voltage transformers (CTs/VTs), essential for accurate measurement and system protection in electrical applications.
Grounding Terminal Identification and Connection
Proper grounding is a critical safety measure in any transformer installation. The first step involves accurately identifying the designated grounding terminal on the transformer itself. Typically, the transformer enclosure will feature a specific grounding lug, often marked with a distinct grounding symbol to ensure easy identification. This dedicated point is engineered to provide a safe path for fault currents, protecting both the equipment and personnel from electrical hazards. Once identified, the next crucial step is the secure connection of the grounding wire. This wire must be firmly attached to the transformer’s grounding terminal. The other end of this grounding conductor is then connected to the main grounding electrode or integrated into the building’s overall grounding system. This establishes an essential equipotential bonding, which is fundamental for system safety and operational reliability. Adhering to manufacturer guidelines and local electrical codes, such as the NEC, is paramount throughout this process. Correct identification and connection prevent dangerous voltage buildup and ensure proper fault current dissipation, making the entire electrical system safer and more stable. This diligent approach to grounding contributes significantly to the longevity of the transformer and the safety of its environment.
Selecting Appropriate Grounding Conductors
Selecting the correct grounding conductor is paramount for transformer safety and code compliance. The size of this conductor must strictly adhere to local electrical regulations, such as the National Electrical Code (NEC) or equivalent international standards. These codes typically specify the minimum conductor size, which is often directly correlated to the size of the transformer’s phase conductors. This correlation ensures the grounding conductor can safely handle the maximum anticipated fault current, allowing protective devices to operate efficiently and prevent equipment damage or hazards to personnel. Material selection is also vital; copper is commonly preferred for its excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance, though aluminum may be used under specific conditions and code allowances. The chosen conductor must provide a continuous, low-impedance path from the transformer’s grounding terminal to the main grounding electrode system. This low-impedance path is crucial for effectively dissipating fault currents and mitigating transient overvoltages, thus enhancing overall system integrity. Always consult the latest edition of relevant electrical codes and engineering specifications to accurately determine the appropriate conductor type and size for each unique transformer installation, ensuring safety and long-term operational reliability.
Wiring Current and Voltage Transformers
Wiring Current Transformers (CTs) and Voltage Transformers (VTs) is fundamental for precise measurement and robust protection in complex electrical systems. For CTs, the primary side connects directly in series with the circuit measuring current, accurately sensing the load current. The secondary side, typically rated for 1A or 5A, then connects to various meters, protective relays, or energy monitors. Crucially, never open an energized CT’s secondary circuit; this induces dangerously high voltages, posing severe risks to personnel and equipment integrity.
Conversely, VTs (Potential Transformers) connect in parallel with the circuit to accurately measure system voltage. Their primary side connects across the power source phases, sensing system voltage, while the secondary side (often 120V) connects to voltmeters, protective relays, or control circuits. Proper wiring ensures safe, reliable unit operation and accurate data. Understanding detailed wiring diagrams, identifying all correct components and their specific connections, and meticulously adhering to specifications like burden calculations, are essential steps. Always refer to the transformer’s specific wiring diagram and master engineer-level protocols, including LOTO (covered separately but contextually relevant) and configuration types like Delta-Wye, for optimal system safety and accuracy.